Data Protection Complaints 2013 – 2014
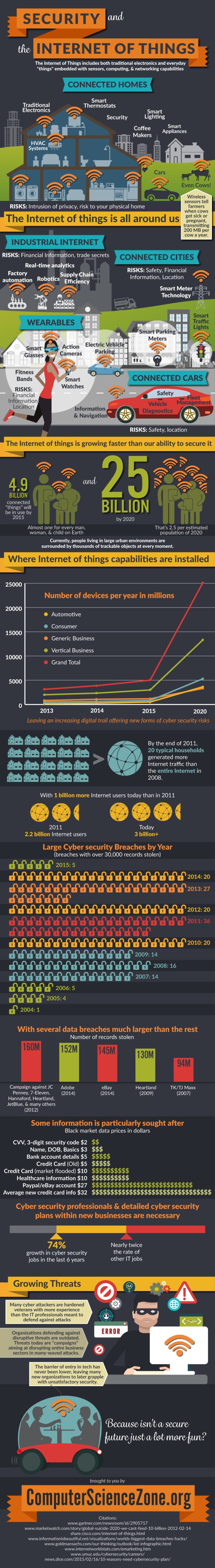
Yesterday I read that the Information Commissioner’s Office handled 259,903 calls to its helpline and has resolved 15,492 data protection complaints last year. This is an increase of 10% over the previous year. And here’s another staggering figure – the ICO received 161,720 reports from people about spam texts and nuisance calls.
Half the total complaints received related to “subject access”, with a range of organisations about whom complaints were made, including lenders, local government, educational providers and local health providers.
The importance of data protection in business
Organisations and businesses can no longer ignore the importance of data protection governance, compliance and security – they now have no choice but to understand and meet their regulatory requirements to avoid the penalties of non-compliance. Last year’s attitude to and handling of ‘subject access requests’ is a perfect illustration of the current complacency seen among some data users.
The sheer volume of personal data being collected physically and digitally every day is multiplying at an extraordinary rate and organisations are continuing to find ever more complicated ways of using data. Use of big data continues to develop with organisations trying to navigate their way through woefully outdated legislation.
The importance of the ICO
As a result, the data protection challenges to business, the consumer and the ICO are spiralling. It’s increasingly important for the data subject to know that a strong, independent body – which means the ICO – can be trusted to keep watch and offer protection.
With this increase in volume and demand, it’s hardly surprising that the ICO is calling for greater powers, greater independence, and additional funding.
Funding is a particularly difficult area as the EU data protection reforms currently propose the removal of the notification requirement and accompanying fees that fund the ICO’s DPA work. Lack of funding will inevitably give rise to cuts in the services provided by the ICO – for example, it has no legal obligation to provide a helpline, and reduced funding makes it unlikely to be able to continue to handle its current – let alone future – volumes of calls a year.
So it’s absolutely vital not only to individuals but also to businesses, organisations, government and the ICO itself that necessary resource, funding, independence and evolving powers are provided to allow the Information Commissioner to continue to protect, update and enforce data protection legislation.
ICO’s internal data security breach
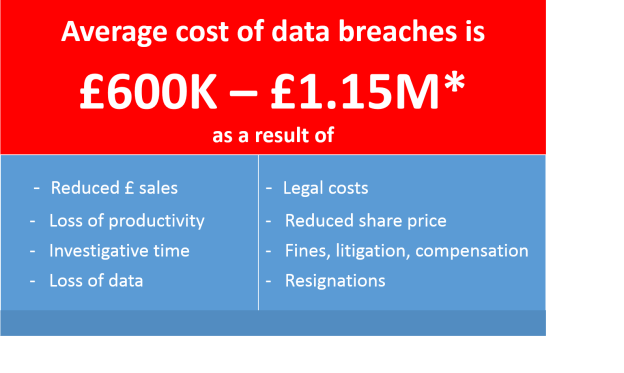
However, it is somewhat unfortunate that at the time the ICO is asking for greater funding, independence and stronger powers, they are also admitting to their own “non-trivial” data breach. The incident was treated as a self-reported breach and was apparently investigated and treated no differently from similar incidents reported to the ICO by others. After an internal investigation the ICO concluded that the likelihood of damage or distress to any affected data subjects was low, and that it did not amount to a serious breach of the Data Protection Act. A full investigation was carried out with recommendations made and adopted.
However, later information suggests that this breach is now linked to a criminal investigation. So the breach investigation has not, seemingly, been closed.
Data Compliant

If you have any concerns over data protection compliance or security, don’t hesitate to get in touch – call 01787 277742 or email victoria@datacompliant.co.uk